Keeping sensitive data safe is non-negotiable. API keys, database credentials, and encryption keys power your infrastructure, and if they’re mishandled, attackers get a doorway into everything, mismanaging them can lead to devastating security breaches.
In this session, we explored practical ways to secure your workloads, automate secrets rotation, and integrate Vault with Kubernetes and CI/CD pipelines.
Check the full webinar here:
Highlights from the Webinar
During the session, we explored practical approaches to securing workloads, automating secret rotation, and integrating HashiCorp Vault with Kubernetes and CI/CD pipelines. Attendees learned practical techniques for implementing zero-trust principles and maintaining strong compliance standards across hybrid and multi-cloud environments.
Integrating Vault with LLMs
Vault offers an MCP server which allows integration of large language models (LLMs) with the HashCorp Vault server. Using Vault MCP server with LLMs enhances the user’s experience by allowing Vault management through simple prompts. Vault MCP server is still in beta but it already offers many ways to manage secrets engines within Vault.

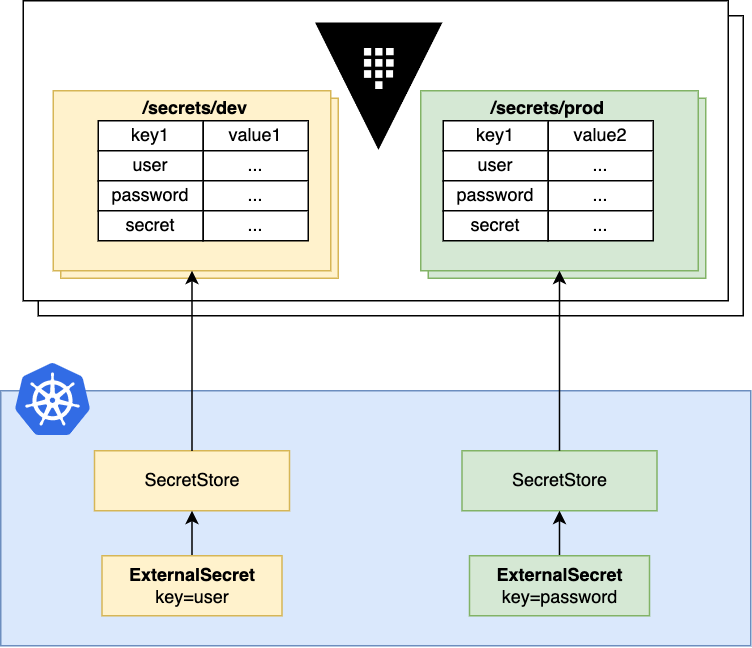
Vault Secrets within OpenShift
Using the external secrets operator, Vault secrets can be automatically fetched within OpenShift, keeping sensitive data secure. Vault centralizes secret management, while external secrets operator ensure your application always have up-to-date credentials without exposing secrets in plain text. There is an alternative as well – Vault Secrets Operator.
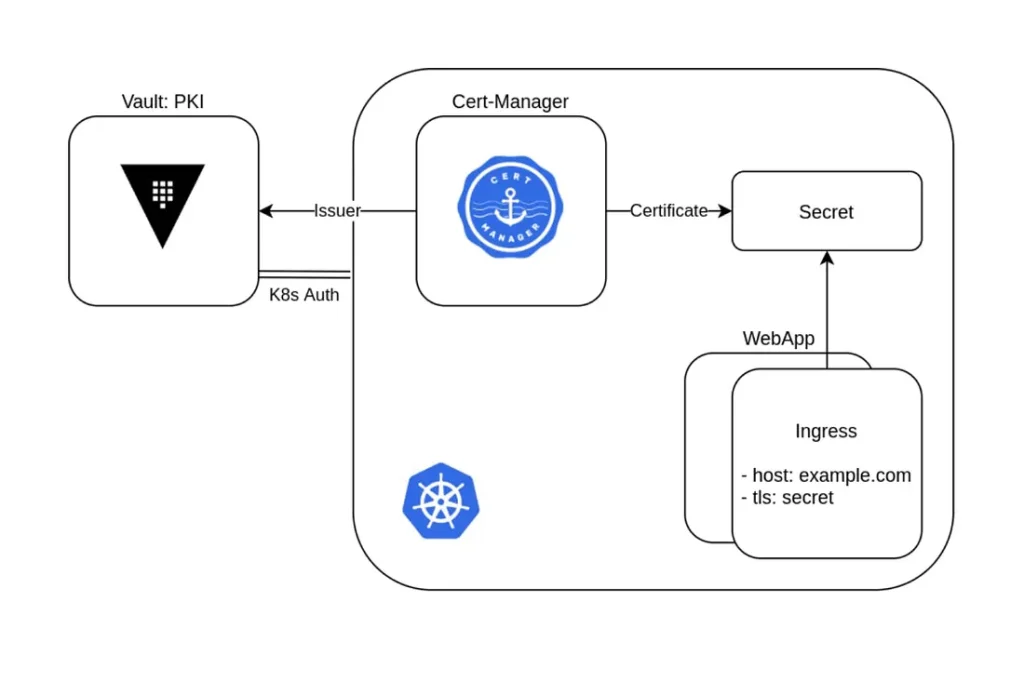
Issuing Certificates within OpenShift and Linux Servers
With certificate validity duration shrinking, Vault’s PKI secrets engine leverages the ACME protocol with tools like Cert-Manager Operator for Red Hat OpenShift and Certbot to automate certificate lifecycle management. Cert-Manager Operator automates issuance and renewal of SSL certificates used by Ingress resources within OpenShift. For applications running outside of OpenShift, Certbot can be used to issue and renew SSL certificates. The initial manual proces of certificate issuance and renewal can be automated.
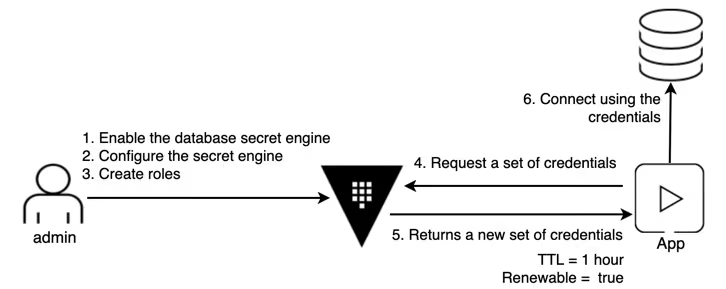
JIT database credentials
Securing databases with long-lived passwords pose a significant security risk. Vault’s dynamic database credentials mitigate this by generating unique, short-term credentials for each database connection created by either a user or an application. Every new set of credentials has a lease attached to it, and each lease has a time-to-live (TTL) set which tells how long credentials are valid for. After the lease expires or gets revoked, the temporary credentials automatically get deleted from the Postgres database. This limits exposure if credentials are compromised and strenghtens overall access control.
Encryption as a service
Vault’s Encryption as a Service centralizes cryptographic operations, offering secure key management and encryption/decryption via APIs. It supports standard algorithms like AES and RSA, enforces strict access controls, and automates key rotation. This reduces implementation complexity, minimizes security risks from misconfigurations, and helps maintain compliance—making encryption simpler and more reliable for developers and security teams alike.

Secrets transformation
Vault offers a transformation engine that secures sensitive data by converting it into masked formats while maintaining its structure. It supports masking, tokenization and format-preserving encryption. Vault transformation engine generates realistic but fake data that looks valid. Only authorized users can perform transformations, ensuring compliance.