There is officially a new major release of Apache Kafka with version 3.0 out right now that brings a big list of changes. Apache Kafka 3.0 introduces a variety of new features, breaking API changes and improvements to Kraft – Kafka’s built-in consensus mechanism that will replace Apache ZooKeeper. Let’s talk about some of the modifications we believe are the most important.
Firstly, there are two major alterations worth mentioning and that is support deprecation for Java 8 and Scala 2.12. From the next major release (4.0), support for these will be removed, which gives users more than enough time to adapt (KIP-750 and KIP-751).
Secondly, we will go over modifications made to clients – including changes made to consumers, producers, and AdminClient. A major change that came with version 3.0 is the ability for Kraft Controllers and Kraft Brokers to generate, replicate and load snapshots for the metadata topic partition named __cluster_metadata, which is used by the Kafka cluster to store and replicate metadata information about the cluster like Broker configuration, topic partition assignment, leadership and so on (KIP-630).
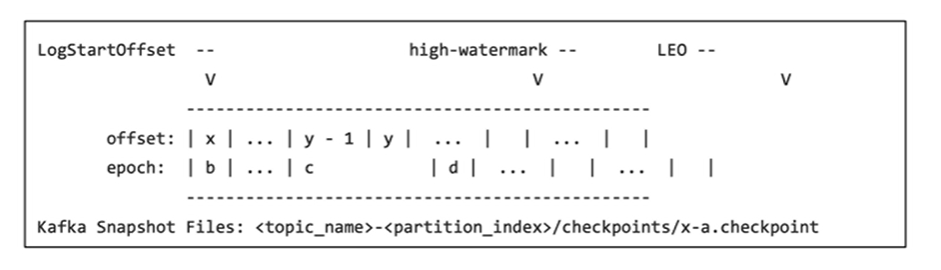
Example of a snapshot as a file on disk
Kafka Controller is now completely taking over the responsibility of generating a Kafka Producer ID and is doing so in both ZooKeeper and Kraft modes (KIP-730). Starting from version 3.0, producers will also enable the strongest delivery guarantee by default, meaning that idempotency and acknowledgment of delivery by all replicas are turned on (KIP-679). Support for reading offsets of multiple consumer groups at the same time within a single request/response is also enabled (KIP-709). New classes that enable serialization and deserialization of generic lists are also added, which is a nice feature for both Kafka clients and Kafka Streams (KIP-466).
Kafka Connect also has some minor changes. Firstly, connector client overrides are enabled by default which wasn’t previously the case (KIP-722). Also, connector log contexts are now enabled by default in the pattern of log4j logs of the Connect worker (KIP-721). Also, Connect API got an improvement. Previously, when a connector or one of its tasks failed, users would call the connector restart API expecting that both the connector and its tasks would restart. However, that was not the case and that only restarted the connector instance and not the failed tasks. That was changed in this release of Kafka (KIP-745) and now the tasks can also be restarted (either all or only failed tasks).

Example of Connect API call
Since we are all big fans of streaming data, we also need to mention changes made to Kafka Streams. None of these are ground-breaking – most of them are minor upgrades. Improvement was done to timestamp synchronization and how Streams tasks choose to fetch records. When Streams are processing a task with multiple inputs, each time it is ready to process a record, it has to choose which input to process next. It always takes from the input for which the next record has the least timestamp. The result of this is that Streams processes data in timestamp order. However, if the buffer for one of the inputs is empty, Streams do not know what timestamp the next record for that input will be. Streams introduced a configuration “max.task.idle.ms” in KIP-353 to address this issue some time back. The config allows Streams to wait for some time for data to arrive on the empty input so that it can make a timestamp-ordered decision about which input to pull from next. However, this config can be hard to use reliably and efficiently, since what we’re really waiting for is the next poll that would return data from the empty input’s partition, and this guarantee is a function of the poll interval, the max poll interval, and the internal logic that governs when Streams will poll again. This was resolved in KIP-695.
Some other changes include adding new methods for Streams applications to keep track of the progress and health of its tasks (KIP-715). Default Streams replication factor was changed from 1 to -1 which allows Streams applications to use the default replication factor defined at the broker level, and that was not the case before (KIP-733).
MirrorMaker v1 is also deprecated from this release onward, and the development of new features and major improvements will focus on MirrorMaker2 (KIP-720).
These are only some of the modifications we think are the most important, but you can check out the whole list of changes here.